Thursday, February 3, 2022
Low Power Low Voltage Bulk Driven Balanced OTA
Handling Trust in A Cloud Based Multi Agent System
Cloud computing is an opened and distributed network that guarantees access to a large amount of data and IT infrastructure at several levels (software, hardware...). With the increase demand, handling clients' needs is getting increasingly challenging. Responding to all requesting clients could lead to security breaches, and since it is the provider's responsibility to secure not only the offered cloud services but also the data, it is important to ensure clients reliability. Although filtering clients in the cloud is not so common, it is required to assure cloud safety. In this paper, by implementing multi agent systems in the cloud to handle interactions for the providers, trust is introduced at agent level to filtrate the clients asking for services by using Particle Swarm Optimization and acquaintance knowledge to determine malicious and untrustworthy clients. The selection depends on previous knowledge and overall rating of trusted peers. The conducted experiments show that the model outputs relevant results, and even with a small number of peers, the framework is able to converge to the best solution. The model presented in this paper is a part of ongoing work to adapt interactions in the cloud.
For more details:https://allconferencecfpalerts.com/cfp/view-paper.php?eno=5261
Wednesday, February 2, 2022
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF HYBRID FORECASTING MODEL IN STOCK MARKET FORECASTING
Author : Mahesh S. Khadka*, K. M. George, N. Park and J. B. Kima
Affiliation : aDepartment of Economics and Legal Studies in Business, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater, OK 74078, USA
Country : USA
Category : Information Technology Management
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 4, 3, August, 2012
Monday, January 31, 2022
Low Power Low Voltage Bulk Driven Balanced OTA
The last few decades, a great deal of attention has been paid to low-voltage (LV) low-power (LP) integrated circuits design since the power consumption has become a critical issue. Among many techniques used for the design of LV LP analog circuits, the Bulk-driven principle offers a promising route towards this design for many aspects mainly the simplicity and using the conventional MOS technology to implement these designs.
For more details:https://allconferencecfpalerts.com/cfp/view-paper.php?eno=5276
Wednesday, January 26, 2022
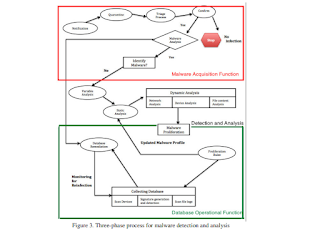
Optimised Malware Detection in Digital Forensics
Author : SaeedAlmarri
Affiliation : University of Bedfordshire
Country : United Kingdom
Category : Networks & Communications
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 6, 1, January, 2014
Abstract :
Keyword : Denial of service (DOS), Wireshark, Netstat, TCPView, The Sleuth Kit (TSK), Autopsy, Digital Forensics, Malware analysis, Framework
Sunday, January 23, 2022
Classification of OCT Images for Detecting Diabetic Retinopathy Disease using Machine Learning
Author : Marwan Aldahami and Umar Alqasemi
Affiliation : King Abdulaziz University
Country : Saudi Arabia
Category : Digital Signal & Image Processing
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 12, 6, December, 2021
Abstract :
Keyword : Image classification, diabetic retinopathy, support vector machine, optical coherence tomography, retina, machine learning.
For more details: https://allconferencecfpalerts.com/cfp/view-paper.php?eno=5274
Monday, January 17, 2022
Sensing Method for Two-Target Detection in Time-Constrained Vector Poisson Channel
Author : Muhammad Fahad and Daniel R. Fuhrmann
Affiliation : Michigan Technological University
Country : USA
Category : Digital Signal & Image Processing
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 12, 6, December, 2021
Abstract :
Keyword : sensor scheduling, vector Poisson channels.
Sunday, January 16, 2022
An Efficient FPGA Implemenation of MRI Image Filtering and Tumour Characterization Using XILINX System Generator
Author : S. Allin Christe, M. Vignesh and A. Kandaswamy
Affiliation : PSG College of Technology
Country : India
Category : Embedded Systems
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 2, 4, December, 2011
Abstract :
Keyword : MRI, Matlab, Xilinx System Generator, FPGA, Edge Detection
Friday, January 14, 2022
The Impact of Mobile Nodes Arrival Patterns in MANETS Using Poisson Models
Author : John Tengviel1, K. A. Dotche2 and K. Diawuo3
Affiliation : 1Department of Computer Engineering, Sunyani Polytechnic, Sunyani, Ghana 2Department of Telecommunications Engineering, KNUST, Kumasi, Ghana 3Department of Computer Engineering, KNUST, Kumasi, Ghana
Country : Ghana
Category : Information Technology Management
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 4, 3, August, 2012
Abstract :
Keyword : MANETs, Mobility models, Mobile nodes distribution, Arrival Patterns, Poisson distribution.
Wednesday, January 12, 2022
Performance Analysis of OLSR Protocol in MANET Considering Different Mobility Speed And Network Density
Author : Koay Yong Cett, Nor Aida Mahiddin*, Fatin Fazain Mohd Affandi, Raja Hasyifah Raja Bongsu and Aznida
Affiliation : Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin (UniSZA)
Country : Malaysia
Category : Networks & Communications
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 13, 6, December, 2021
Abstract :
Keyword : MANET, OLSR, Node Mobility, Density, Routing Scheme
Tuesday, January 11, 2022
Multi-carrier Equalization by Restoration of RedundancY (MERRY) for Adaptive Channel Shortening in Multi-carrier Systems
Author : Samir Abd Elghafar
Affiliation : Menoufia University
Country : Egypt
Category : Networks & Communications
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 5, 6, November, 2012
Abstract :
Keyword : DFT, DMT, DST
Sunday, January 9, 2022
Analysing the Correlation of Geriatric Assessment Scores and Activity in Smart Homes
Author : Björn Friedrich, Enno-Edzard Steen, Sebastian Fudickar and Andreas Hein
Affiliation : Carl von Ossietzky University
Country : Germany
Category : Computer Science & Information Technology
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 12, 1/2, April, 2021
Abstract :
Keyword : ubiquitous computing, biomedical informatics, health, correlation, piecewise linear approximation
Friday, January 7, 2022
Adaptive Noise Reduction Scheme for Salt and Pepper
Author : Tina Gebreyohannes and Dong-Yoon Kim
Affiliation : Ajou University
Country : South Korea
Category : Digital Signal & Image Processing
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 2, 4, December, 2011
Abstract :
Keyword : MAG, Directional filtering, Noise detection, Noise reduction
Thursday, January 6, 2022
A Design Science Approach to Develop a New Comprehensive SOA Governance Framework
Author : Fazilat Hojaji and Mohammad Reza Ayatollahzadeh Shirazi
Affiliation : Amirkabir University of Technology
Country : Iran
Category : Information Technology Management
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 4, 3, August, 2019
Abstract :
Keyword : SOA governance, service lifecycle, SOA roadmap, SOA adoption, COBIT
Wednesday, January 5, 2022
Performance Analysis of Transport Layer Basedhybrid Covert Channel Detection Engine
Author : Anjan K
Affiliation : R V College of Engineering
Country : India
Category : Networks & Communications
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 5, 6, November, 2013
Abstract :
Keyword : Covert Channel, Subliminal Channel, Hybrid Covert Channel,Network Security, Trapdoors
Tuesday, January 4, 2022
OptAGAN: Entropy-based Finetuning on Text VAE-GAN
Author : Paolo Tirotta
Affiliation : University of Bologna
Country : Italy
Category : Computer Science & Information Technology
Volume, Issue, Month, Year : 11, 23, December, 2021
Abstract :
Monday, January 3, 2022
Detection and Removal of Non-Responsive Channels and Trials in Evoked Potentials Using Median Test